AAD 2023
Secukinumab for Pediatric Psoriasis Treatment
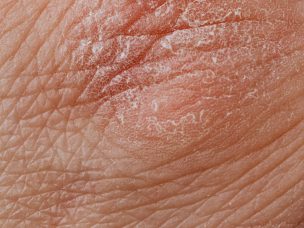
Secukinumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that targets IL-17A, is a promising treatment option in pediatric patients aged 6 years and above with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Psoriasis is a chronic and inflammatory skin disease that affects 1% to 5% of the global population. It is caused by T-cell activity and genetic and epigenetic...
Phototherapy for Skin Diseases, Cancer, and Allergies
Phototherapy is a promising treatment option for various skin conditions, but further research is needed to explore its full potential and safety. Non-invasive phototherapy using LED technology is becoming popular for medical and aesthetic dermatological conditions. Studies have shown that these treatments can promote wound healing and reduce inflammation. Recent studies using blue light have...
Diet-Induced Inflammation Not Linked to Psoriasis
Dietary inflammatory index not linked to psoriasis in participants with different population settings Diet-induced inflammation seems not to be associated with psoriasis, according to a study published online Jan. 26 in the Journal of Dermatology. Nouzhou Liu, from Sichuan University in Chengdu, China, and colleagues examined the association between the dietary inflammatory index (DII) and incident...
AI Model Differentiates Scalp Psoriasis From Seborrheic Dermatitis
A deep learning (DL) model based on dermatoscopic images can differentiate scalp psoriasis from seborrheic dermatitis, according to a study recently published in Frontiers in Medicine. Zhang Yu, from Inner Mongolia Medical University in Hohhot, China, and colleagues developed a new diagnostic method for discriminating scalp psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis based on a DL model. A...
Atopic Dermatitis in Skin of Color Webcast
In this MD Newsline webcast Dr. Pete Thomas and Dr. Joyce Imahiyerobo-Ip discuss atopic dermatitis in skin of color. Register here to view the webcast. Visit MDNewsline.com’s atopic dermatitis channel for more information on atopic dermatitis.
The Psychosocial Burden of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata causes patchy hair loss and can affect patients emotionally, leading to higher rates of depression and anxiety and reduced quality of life. Scalp hair is more than just a biological feature; it is an integral aspect of self-identity and cultural expression. However, hair loss can be a significant source of emotional distress and...
Low-Dose Interleukin-2 for Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Low-dose IL-2 treatment may provide a new option for patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria who do not respond to traditional therapies. Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) can significantly impact patients’ quality of life, and a substantial proportion remains unresponsive to traditional therapies. While second-generation H1-antihistamines are the first-line treatment, they may only be effective for some...
Genetic, Environmental, Prenatal Risk Factors Play Role in Early Atopic Dermatitis
Nonmodifiable risk factors include gestational diabetes, maternal history of allergy, prenatal history of eczema Genetic and environmental prenatal risk factors play a role in early childhood atopic dermatitis (AD), according to a review published online Jan. 27 in the Annals of Dermatology. Hong Cui, M.D., Ph.D., from the First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional...
Alopecia Areata After COVID-19 Infection and Vaccination
Rarely, some individuals may develop symptoms of alopecia areata following COVID-19 infection or vaccination, which are associated with pro-inflammatory cytokines that are also implicated in the pathogenesis of alopecia areata. Alopecia areata (AA) concerns have emerged following COVID-19 vaccination and infection. This cross-sectional analysis evaluated the relationship between COVID-19 infection or vaccination and AA. The...
More Medical News