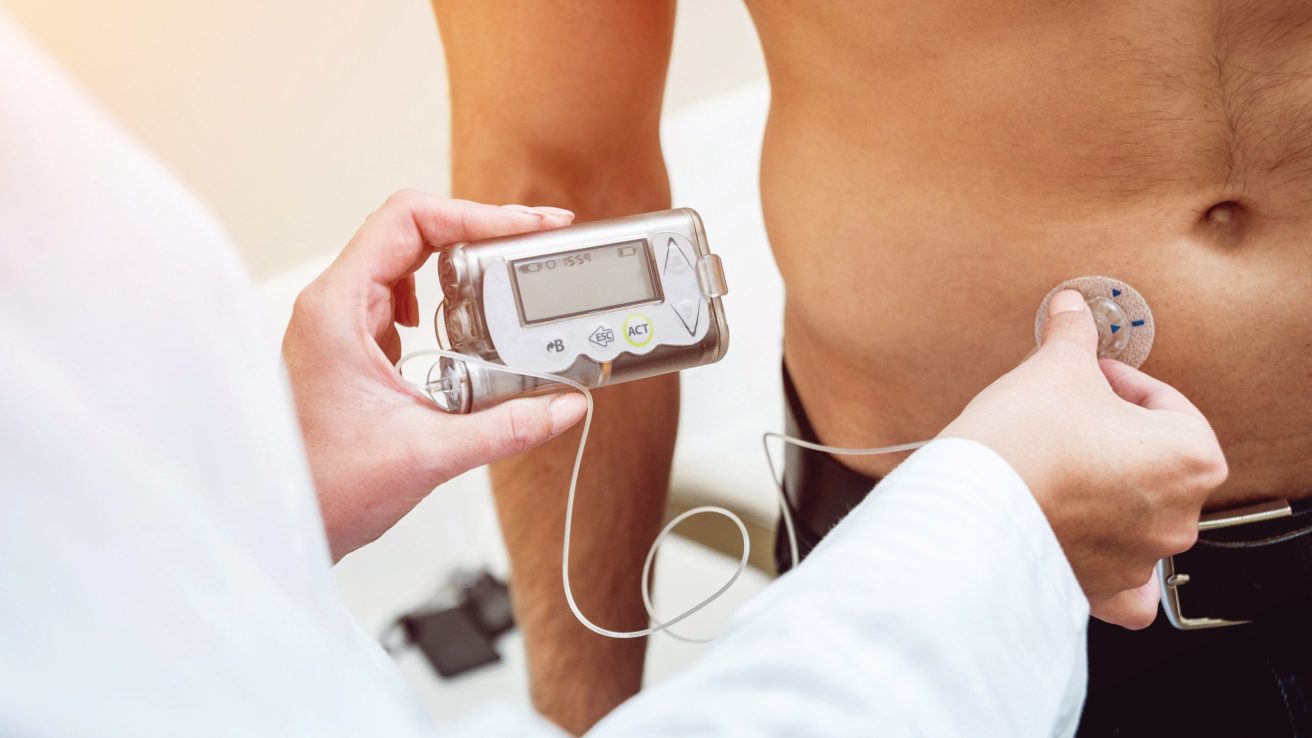
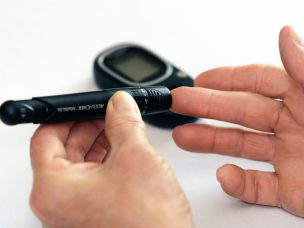
WEDNESDAY, Dec. 30, 2020 (HealthDay News) — On average, glycemic control improved during lockdown among people living with type 1 diabetes, according to a study published online Dec. 23 in Diabetes Care.
Louis Potier, M.D., from Bichat Hospital in Paris, and colleagues conducted an observational assessment from a self-reported questionnaire on behavioral changes and glycemic information from flash glucose monitoring (FGM) during lockdown in 1,378 individuals living with type 1 diabetes. Change in the mean glucose level two months before and one month after the lockdown was the main outcome.
The researchers observed improvement in mean glucose from 9.1 ± 1.7 mmol/L to 8.7 ± 1.7 mmol/L. Decreased alcohol consumption, an increase in the frequency of FGM scans and in the number of hypoglycemic events, and an easier diabetes control perception were factors associated with better glycemic control (odds ratios, 1.75, 1.48, 1.67, and 1.71, respectively).
“Our study suggests that while the lockdown was a source of anxiety for many people with type 1 diabetes, it was also an opportunity to make positive behavioral changes,” the authors write. “Their persistence after easing of lockdown should be studied.”
Several authors disclosed financial ties to the biopharmaceutical and medical device industries.
Abstract/Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)