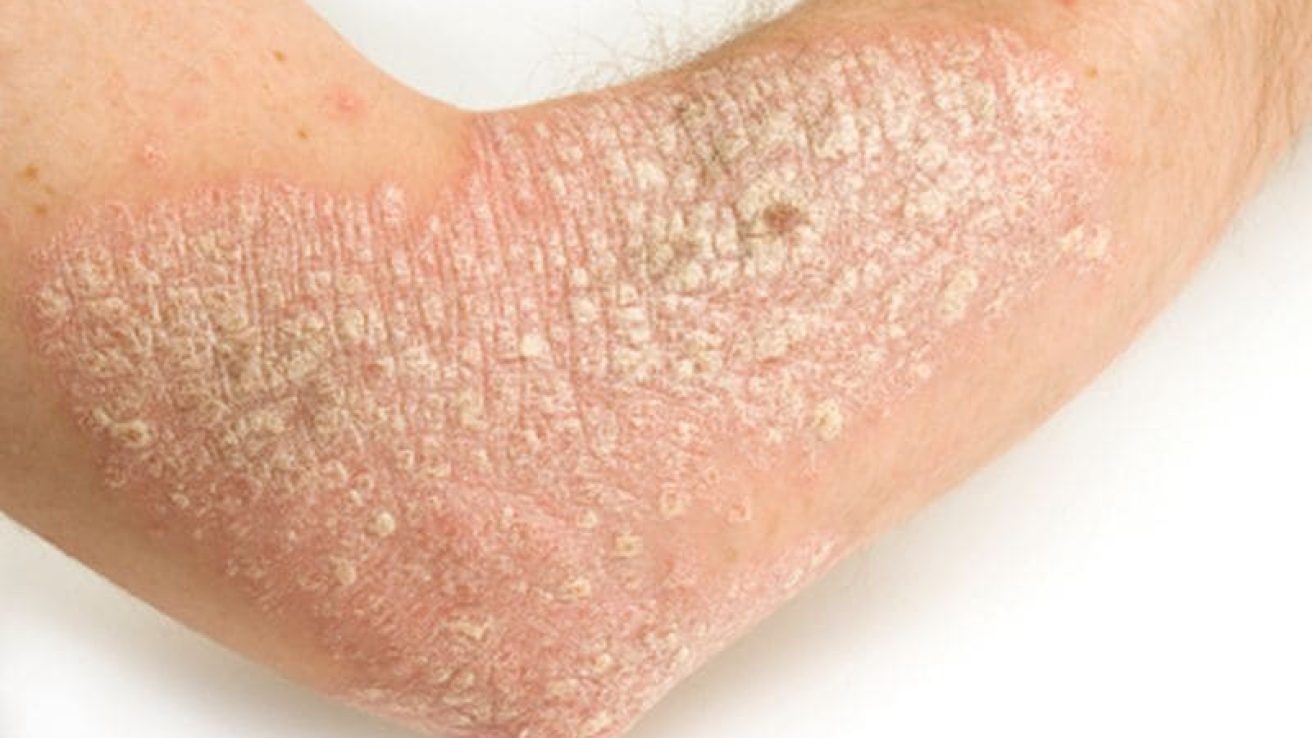
TUESDAY, Sept. 15, 2020 (HealthDay News) — For patients with psoriasis, lipid-rich necrotic core (LRNC) is associated with psoriasis severity and cardiovascular risk factors and is reduced for those patients receiving biologic therapy, according to a study published online Sept. 15 in Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging.
Harry Choi, M.D., from the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland, and colleagues characterized LRNC in 209 biologically naive psoriasis patients who underwent coronary artery computed tomography angiography at baseline and one year. Histopathologically validated software was used to assess changes in LRNC before and after biologic therapy over one year.
The researchers found that LRNC was associated with Framingham risk score and psoriasis severity in all participants at baseline. At one year, a reduction in LRNC was seen in participants receiving biologic therapy (3.12 versus 2.97 mm²), while no significant change was seen for those who did not receive biologic therapy (3.12 versus 3.34 mm²). Compared with the change in the non-biologic-treated group, the change in LRNC in those receiving biologic therapy was significant (−0.22 versus 0.14 mm²); after adjustment for cardiovascular risk factors and psoriasis severity, the change remained significant.
“We specifically demonstrated the beneficial effects of biologic therapy on LRNC, and these findings provide important insight into the potential stabilization and reversibility of LRNC in the coronary artery,” the authors write.
Several authors disclosed financial ties to the biopharmaceutical industry.
Abstract/Full Text (subscription or payment may be required)